
Developing Adaptive Systems and Add-on’s in the 4IR
The 4th Industrial Revolution is the first industrial revolution that introduced a paradigm shift focused on the generation of market value. It fostered adaptiveness and customer orientation in businesses.
This required developing adaptive interfaces that allow introducing adaptive cognitive add-ons in existing systems.
Technological Framework
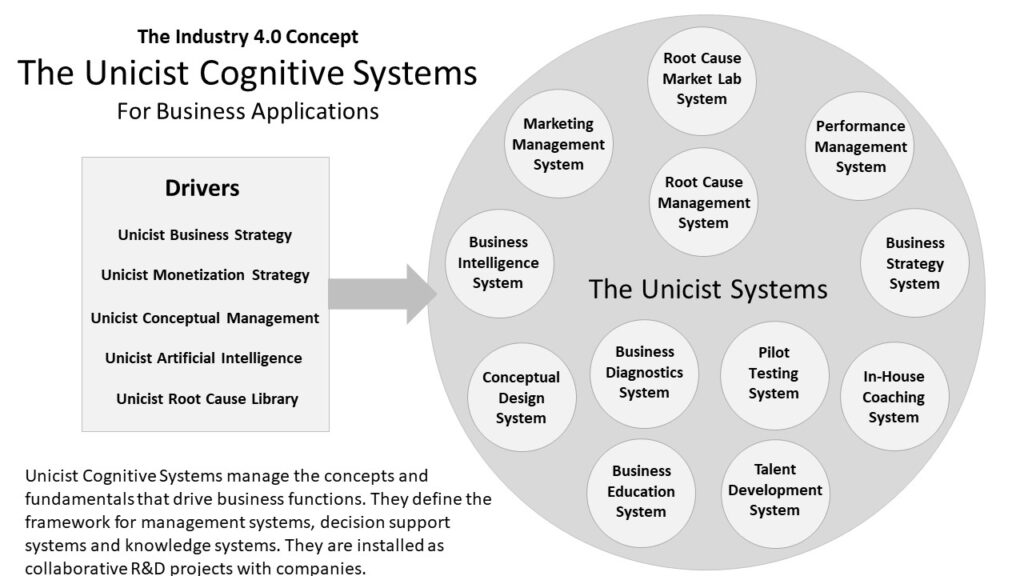
Unicist AI
The Unicist Artificial Intelligence implies the integration of data-based AI and fundamentals-based AI. On the one hand, the categories defined by fundamentals-based AI provide the autonomous universes that are needed to minimize the subjective biases of data-based AI.
Automation & Robotics
The unicist ontology of automation implies a process that integrates systemic, operational, and cognitive objects with quality assurance through automated processes or human control.
Work-station Design
The specific WSD requires defining the efficacy that needs to be available, the efficiency of the system and the necessary level of automation according to the characteristics of the adaptive aspects of a job.
Telework Organization
Home-office telework is a different context for work, which requires having a system that is functional based on the context of home-office. It requires working with systems to manage the accountability, reliability and transparency of the roles of the people involved and these work processes.
Participative R&D Projects
The implementation of the adaptive systems is based on the development of participative R&D projects that ensure their functionality and allow transferring the technology.
The first prototype begins to work within 45 days. It requires the participation of an internal strategic analyst. All the projects are based on the generation of positive cashflow for the clients.
Strategic Analysts
The use of adaptive Strategic Analysts might be an additional role for existing process analysts in a company. Strategic analysis is centrally focused on empowering the generation of value while reducing costs. In companies that manage big data, the strategic analyst is a natural counterpart of the data scientists.